In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): What Is It?
IVF (In vitro fertilisation) is an assisted reproductive technology in a process by which egg and sperm are fertilized outside the body and then placed in a woman’s uterus after fertilisation. It usually involves the removal of eggs from the woman’s ovary and the collection of sperm from a male. The embryo, which results from fertilisation in the laboratory, is transferred to the woman’s uterus about two to five days later. At this stage, long before any organs have formed, it is still visible to the naked eye and consists of only a few cells.
IVF has had huge publicity and has gained a false reputation as the solution for infertili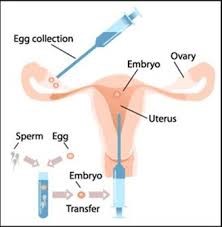 ty. In practise, it is one of the most demanding of all procedures in reproductive medicine and is the least successful compared to some alternatives. Strictly speaking, IVF is not even a “treatment” for infertility as it does not alter the underlying cause of infertility. It is simply an attempt to help someone who is infertile to have a baby, the attempt can be repeated several times, but the basic cause of infertility remains. Although IVF does not change the underlying cause of fertility, it is best where possible to seek therapy which may improve the chances of becoming pregnant naturally. But there is no doubt that IVF has revolutionized the treatment of infertile people and increased our knowledge about many aspects of what initially causes infertility.
ty. In practise, it is one of the most demanding of all procedures in reproductive medicine and is the least successful compared to some alternatives. Strictly speaking, IVF is not even a “treatment” for infertility as it does not alter the underlying cause of infertility. It is simply an attempt to help someone who is infertile to have a baby, the attempt can be repeated several times, but the basic cause of infertility remains. Although IVF does not change the underlying cause of fertility, it is best where possible to seek therapy which may improve the chances of becoming pregnant naturally. But there is no doubt that IVF has revolutionized the treatment of infertile people and increased our knowledge about many aspects of what initially causes infertility.
Why is IVF used?
- Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes
- Male factor infertility including decreased sperm count or sperm motility
- Women with ovulation disorders, premature ovarian failure, uterine fibroids
- Women who have had their fallopian tubes removed
- Individuals with a genetic disorder
- Unexplained infertility
Factors to Consider with In Vitro Fertilization
- Age: Any woman who is still ovulating may try IVF, although success rates decline as a woman ages. Women under age 35 have the greatest chance of success with this technique.
- Multiple births:Generally, in women who use IVF to establish a live birth, about 63% are single babies, 32% are twins, and 5% are triplets or more.
- Cost:IVF is a costly procedure that, in many cases, is not covered by health insurance plans.
- Reduced need for surgery:If a woman has IVF, she may not have to undergo surgery on her Fallopian tubes. It is estimated that the IVF technique has reduced such surgeries by half.
- Safety:Studies suggest that in vitro fertilization is safe. A study covered nearly 1,000 children conceived through these methods in five European countries and found that the children monitored from birth to age 5 years, were as healthy as children conceived naturally. However, other studies have found a slightly increased risk of genetic disorders in children conceived through assisted reproductive technologies. However, adverse outcomes during pregnancy and the prenatal period are higher in pregnancies that resulted from IVF. Some or most of this increased risk is due to the fact that a greater proportion of IVF pregnancies involve multiple gestations. However, there is a slight increased risk of complications in singleton pregnancies resulting from IVF, possibly related to the age of the parents or to the underlying conditions which led to the infertility and need for IVF.
In Vitro Fertilization Performance
IVF helps people with infertility who wants to have a baby. IVF is expensive and invasive, so couples often try other fertility treatments first. These may include taking fertility drugs or having intrauterine insemination. During that procedure, a doctor transfers sperm directly into a woman’s uterus.
Infertility issues for which IVF may be necessary include:
- reduced fertility in women over the age of 40
- blocked or damaged fallopian tubes
- reduced ovarian function
- endometriosis
- uterine fibroids
- male infertility, such as low sperm count or abnormalities in sperm shape
- unexplained infertility
Parents may also choose IVF if they run the risk of passing a genetic disorder on to their offspring. A medical lab can test the embryos for genetic abnormalities. Then, a doctor only implants embryos without genetic defects.
What is the IVF treatment procedure?
The initial steps for both IVF and ICSI are similar. Both treatments differ in the insemination methodology post the egg collection step.
Step 1: Pre-investigation to assess feasibility
Pre Treatment Investigations
Before subjecting a couple to the IVF procedure they are advised to undergo certain investigations to check the feasibility for the procedure.
The female partner is asked to undergo certain hormonal blood tests and the male partner is asked to undergo basic semen analysis. Both the partners are subjected to certain common tests like blood grouping, HIV, Hepatitis B & C, and blood tests for sexually transmitted diseases as part of the IVF process.
Step 2: Long or Short protocol
Following the pre-assessment, the next step could either be a long protocol or a short protocol. The doctor takes a call on what treatment needs to be followed.
Long Protocol
The duration of the treatment is about one month and can be divided into two phases mainly:
Suppression Phase: The female partner is required to come to the hospital for a daily subcutaneous injection usually from day 22 of the cycle (day 1 is the first day of the menstrual period) for about 15 days.
Stimulation Phase: After about 15 days other set of injection/s is/are added which stimulates the ovaries to produce eggs. These injections are administered by daily injection subcutaneously (sc) or intramuscularly (im) (into the buttock muscle).The daily dose may be increased or decreased depending on how well the ovaries are responding. Stimulation continues until the eggs are mature. This takes approximately 10 – 14 days.
Short Protocol
This usually takes about 15-18 days where injections and medications are administered to the female partner on an everyday basis. This continues until the eggs are mature.
Step 3: Egg Collection
Based on the doctor’s assessment, a date is fixed for egg collection and the female partner’s eggs are removed under vaginal ultrasound guidance. There are no cuts on the abdomen.
Step 4: Semen Preparation and Embryo Transfer
The male partner’s semen is taken and IVF (where eggs are just mixed with sperm) or ICSI (where single sperm is injected into the egg) is carried out in the laboratory. This is then inseminated into the female partner’s uterus.
How are the procedures done?
Egg Collection:
Egg collection is a day care procedure which requires the patient to get admitted to the hospital for half a day. She would be evaluated by anaesthesiologist a day or two prior to the egg collection. The eggs collected under vaginal ultrasound guidance are placed in an incubator. Generally most of the follicles will carry a mature, healthy egg. However, not all follicles may yield an egg, or some may be immature or deteriorating and are thus are unlikely to fertilize normally. It’s very rare that no eggs are found. If the treatment cannot proceed because no eggs can be collected or the egg quality is poor, the doctor will discuss the probable causes of this with you and recommend an appropriate course of action.
Embryo Transfer:
The procedure is carried out by insetting a speculum into the vagina and cleaning the cervix. The patient may feel one cramp as an outer catheter is placed through the cervix into the lower segment of the uterus. A fine plastic catheter, into which the Embryologist has transferred the embryos, is then placed through the outer transfer catheter and advanced near the top of the uterus. The sonographer will visualize the lining of the uterus and guide the physician in the placement of the catheter. Once the placement is correct, the embryos will be expelled from the catheter and inserted into the uterus.
After embryo transfer, the woman may be told to rest for the remainder of the day. Complete bed rest is not necessary, unless there is an increased risk of OHSS. Most women return to normal activities the next day.
After effects of procedure
Women who undergo IVF must take daily shots or pills of the hormone progesterone for 8 to 10 weeks after the embryo transfer. Progesterone is a hormone produced naturally by the ovaries that helps thicken the lining of the womb (uterus). This makes it easier for the embryo to implant. Too little progesterone during the early weeks of pregnancy may lead to miscarriage.
About 12 to 14 days after the embryo transfer, the woman will return to the clinic so that a pregnancy test can be done.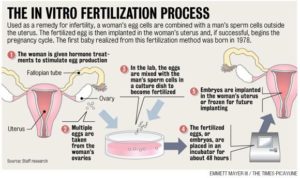
Call your health care provider right away if you had IVF and have:
- A fever over 100.5°F (38°C)
- Pelvic pain
- Heavy bleeding from the vagina
- Blood in the urine
Other Assisted Reproduction Techniques
Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT): Gamete intrafallopian transfer is similar to IVF. It is used when a woman has at least one normal Fallopian tube. Eggs are placed in this tube along with a man’s sperm to fertilize there. This accounts for only about 2% of assisted reproductive technology procedures in the US. Some couples opt for this procedure if they object to fertilization that occurs outside the woman’s body.
Zygote intrafallopian transfer (ZIFT): Zygote intrafallopian transfer is tubal embryo transfer in whom a woman’s eggs are taken from her ovaries, fertilized in the laboratory, and put back in the Fallopian tubes rather than the uterus. ZIFT is even less common than GIFT, making up less than 1.5% of assisted re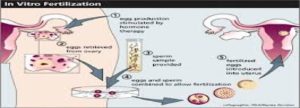 productive procedures.
productive procedures.
Embryo cryopreservation (frozen fertilized egg and sperm) is available when more embryos are created than are transferred to the woman’s uterus. These can be transferred during a future cycle. In this case a woman would take medications to prepare her uterus to receive the embryos at the appropriate time.
Complications Associated with In Vitro Fertilization
As with any medical procedure, there are risks associated with IVF. Complications include:
- multiple pregnancies, which increases the risk of low birth weight and premature birth
- miscarriage (pregnancy loss)
- ectopic pregnancy (when the eggs implant outside the uterus)
- ovarian hyper stimulation syndrome (OHSS), a rare condition involving an excess of fluid in the abdomen and chest
- bleeding, infection, or damage to the bowels or bladder (rare)
Some side effects of fertility medications may include:
- Headaches
- Mood swings
- Abdominal pain
- Hot flashes
- Abdominal bloating
- Success Rates for In Vitro Fertilization
What if I don’t produce healthy eggs or my husband is sterile?
You may choose to use donor eggs, sperm, or embryos. However, make sure to talk with a counsellor experienced with donor issues. You will want to be informed about various legal issues related to gamete donation including the legal rights of the donor.
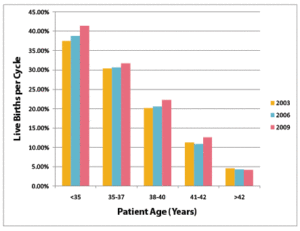
The live birth rate for one cycle varies by maternal age. According to the Society of Assisted Reproductive Technologies (SART):
- The live birth rate per IVF cycle is 40%-43% among women younger than 35 years of age and 33%-36% for those aged 35 to 37 years.
- The success rate ranges from 13%-18% in those older than 40 years of age.
- Pregnancy in women older than 44 years of age is rare.
- When reviewing statistics for different IVF programs, it is important to understand what is actually being reported. A pregnancy rate may include so-called chemical pregnancies, in which the pregnancy test is positive but the pregnancy ends before a viable foetus can be demonstrated by ultrasound. Pregnancy rate is also different from the live birth rate, since it includes all pregnancies that may or may not lead to a live birth. Even live birth rates may vary among different clinics because of selection criteria for patients and the number of embryos typically transferred.
- The rate of miscarriages with IVF pregnancies is the same as that with normally conceived pregnancies. Ectopic pregnancy occurs in about 3% to 5% of cases. An ectopic pregnancy is a serious condition that requires emergency medical care. The embryo is growing outside the uterus and does not survive. RARE: Ovarian hyper-stimulation syndrome (OHSS)
